Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease
Studies demonstrate that stem cell therapy is a promising approach to treating Alzheimer’s Disease. With research supported by the Alzheimer’s Society and protocols used in many clinical studies, the intrathecal and intravenous transplanting of millions of pluriptent mesenchymal stem cells could repair brain damage caused by neurological conditions, such as dementia caused by Alzheimer’s, stroke, or other conditions. That is why stem cells could become a viable and sought-after treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease.
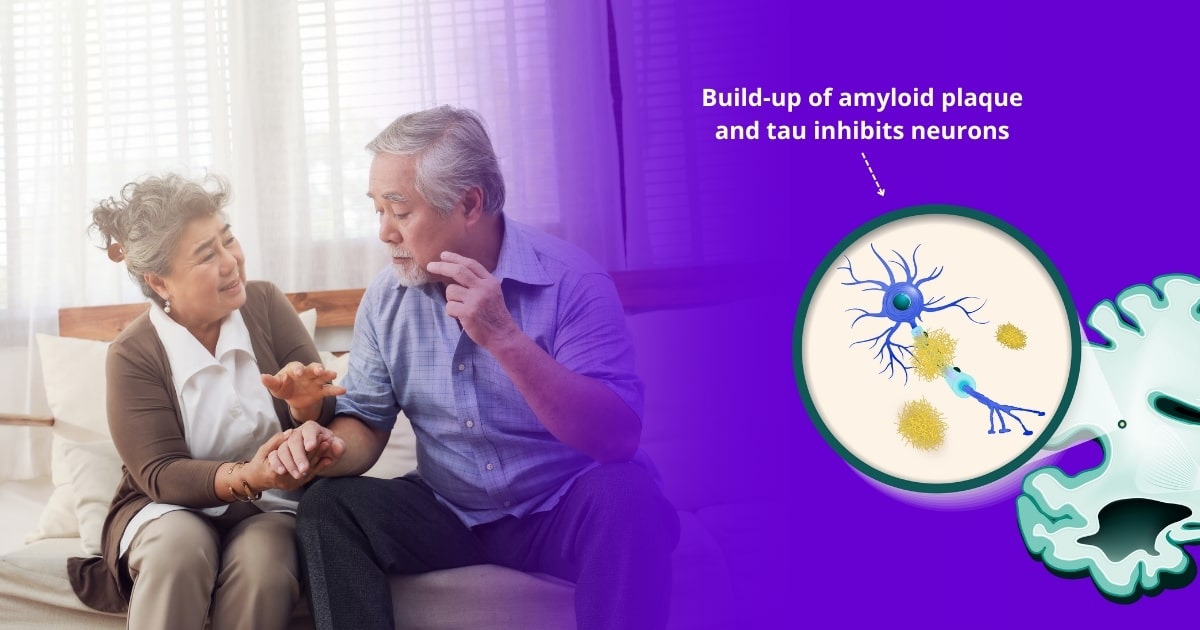

Alzheimer’s is a neurological disease characterized by a progressive decline of mental faculties
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a chronic disease that progressively destroys memory and other mental functions needed for logical thinking, communication, and motor function. Early-onset is rare and occurs between the ages of 30 and 60. Late-onset is most common and occurs after the age of 60-65.
Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia, which is a group of conditions that impair brain functions such as judgment and memory. Generally, Alzheimer’s is associated with mild, moderate, or severe stages of memory loss and decline of cognitive abilities.
There is no known cure for Alzheimer’s and its symptoms worsen over time and are severe enough to impair one’s ability to complete daily tasks and to care for oneself independently. The majority of people diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease are 65 years of age and older. As the condition worsens into the final stages, patients lose the ability to respond to their environment and speak coherently, so they may require hospice care toward the end of their lives.
In the United States, this neurological disease is the 7th leading cause of death. Although a person with Alzheimer’s can reportedly live for about another 20 years, they live for 4 to 8 years on average after being diagnosed. For this reason, additional treatments are currently being researched to find effective treatments for this disease.
What causes Alzheimer’s?
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still not fully understood but it can include a combination of:
- Previously healthy neurons stop functioning, lose connection with other neurons and die.
- Decay in brain cells due to aging, brain damage, inflammation, and autoimmune response.
- Inherited genetic factors and preexisting conditions that inhibit proper delivery of blood, nutrients, and glucose.
- Poor health, exposure to pollutants, and lifestyle choices.
It is also believed that Alzheimer’s disease may result from the abnormal build-up of amyloid and tau proteins that interfere with and impair proper function of brain cells such as neurons. This is a known symptom of Alzheimer’s, yet it has not been proven to be the cause because we can’t yet explain what causes this build-up in the first place.
Although often associated with aging, the reality is that Alzheimer’s disease is not a normal sign of aging. It is the result of changes in the brain that start years before symptoms become apparent and eventually destroy brain cells needed for daily function.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease?
Cognitive Decline
Memory loss, impaired decision-making, confusion in the evening hours, disorientation, forgetfulness, short attention span, making things up, mental confusion, difficulty concentrating, inability to create new memories, inability to learn new things, inability to do simple math, inability to recognize loved ones, inability to recognize common things
Behavioral Symptoms
Repeating questions and own words, poor judgment, difficulty with self-care, uncooperativeness, restlessness, lack of restraint, wandering and getting lost, increased sleeping, loss of bowel and bladder control, inability to combine muscle movements, jumbled speech, loss of appetite
Psychological Changes
Changes in personality, mood swings, tearfulness, impulsiveness, depression, anxiety, hallucination, delusion, paranoia, anger, apathy, general discontent, loneliness, aggression, agitation, irritability
Request an in-person or virtual consultation with a medical specialist to review medical history, lab results, MRIs, and determine eligibility for stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease.
Can stem cells be used to treat Alzheimer’s Disease?
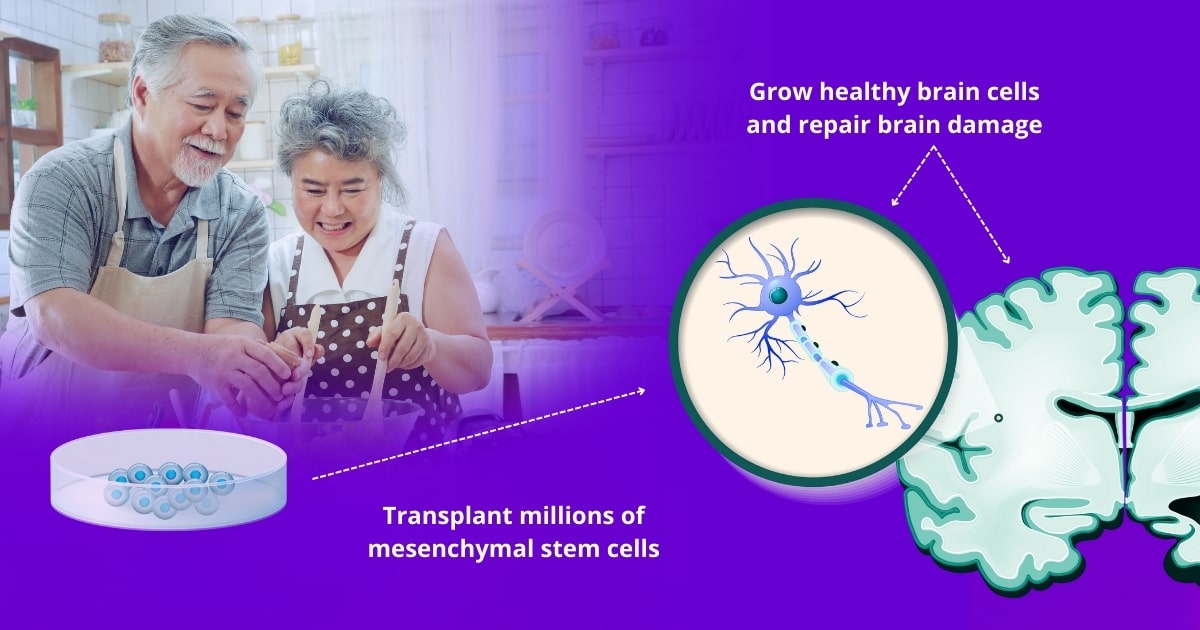
Studies show mesenchymal stem cells can slow Alzheimer’s progression and repair brain damage
Stem cells could be used to treat neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s because umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells have the potential to grow into new healthy brain cells, thus repairing brain damage and restoring proper brain function as well as slowing down the progression of dementia.
Stem cell treatment for Alzheimer’s may involve intravenous and spinal cord injection of up to 800 million vibrant pluripotent stromal mesenchymal stem cells (ideally 3 million MSCs / kg of body weight) as well as alternative and regenerative treatments. It is anticipated that these cells will travel to the brain and begin creating new healthy brain cells—including neurons—and strengthen blood vessels in the brain.
Ethics & safety
Using stromal mesenchymal stem cells derived from healthy bone marrow of screened patients (either oneself or an eligible donor) does not raise ethical concerns since the cells are not from discarded in vitro embryos or other questionable sources. Stem cells have been used successfully for years in several clinical studies to significantly slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in patients of all stages and improve quality of life.
Federal regulations
Is it legal to get stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, our clinic is federally licensed, so all of our treatments are legal and are performed by qualified medical professionals. Other clinics get stem cells delivered from a third-party lab which causes degradation of stem cells through hours of transit. Because we would never jeopardize patients’ wellbeing or our long-standing reputation, we have our own private laboratory to harvest and administer stem cells immediately upon preparation to ensure maximum bioavailability for our patients.
Our private laboratory abides by the and application centers abide by the highest international standards such as COFEPRIS and ISO class 5 and 6. Our clinic is accountable to the COFEPRIS and strictly adheres to proven clinical standards.
Long-lasting results
Stem cells don’t do miracles, but they can far exceed traditional treatments for Alzheimer’s. Patients from all over the globe have successfully received stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease to regenerate brain cells, nerve cells, and improve neurological function. The medical field and research have evolved, making stem cell therapy available to you too.
Private Healthcare
Does insurance cover stem cells?
Insurance companies usually do not cover stem cell therapy unless they are for treating certain blood disorders such as a transplant of bone-marrow stem cells to treat leukemia.
It’s important to note that many European and Asian countries have advanced treatments not currently approved for use in the USA. As news spreads about athletes, celebrities, and prestigious professionals undergoing stem cell therapy, treatments options are likely to become less accessible and increasingly privileged.
Unburdened by profit-driven insurance companies, our doctors are able to stay committed to their oath-bound responsibility and never perform unnecessary treatments under the pretense of securing funding. We perform extensive lab work to determine patient eligibility and identify the best application technique and the right quantity of stem cells that will benefit each patient individually.
Thanks to advances in medicine and scientific research, private sector stem cell therapy such as this is today more accessible in terms of travel, price, and quality.
Alzheimer’s: Traditional Treatment Compared to Stem Cell Therapy
- Multiple specialties: geriatrics, general medicine, neurologist, psychologist, physical therapist.
- Pharmaceutical drugs to increase cognitive enhancement.
- Medication to lower blood pressure and to prevent intracranial clots.
- Antipsychotic drugs to balance mood and reduce uncooperativeness.
- Physical exercise to improve cardiovascular strength and promote healthy brain synapses.
- Hospice care is sought in advanced stages as the condition worsens.
- Cost ranges from $10,400 to $34,517 USD per patient annually in MCOs. Costs increase as the disease worsens year after year.
Because there is no known cure for Alzheimer’s, and it worsens over time, treatment typically consists of cognitive enhancing medication and symptom management. Due to the fact that it is very difficult for an adult patient to generate new healthy brain cells in large quantities fast enough to counteract progression of the disease, the objective of this medical approach is to provide temporary relief to patients.
- Requires specialist care. May be performed in parallel with current medication.
- Involves administering up to 800 million vibrant mesenchymal stem cells via a single spinal cord (intrathecal) injection, intravenously, and other alternative and regenerative treatments.
- Regrow functional new brain cells continually for 6-18 months.
- New cells replace dying or damaged cells to restore synapses.
- Vascular health also is strengthened.
- Flow of nutrients and oxygen to the brain improves.
- Intravenous serums nourish and activate the stem cells.
- Cellular therapies such as exosomes help regulate cell differentiation.
- Cost ranges from $4000 to $25,000 per treatment. A single treatment can provide improvement and delay progression for up to 3 years for early stages.
With research supported by the Alzheimer’s Society and protocols used in many clinical studies, MCSs have the potential to repair brain damage caused by Alzheimer’s. While stem cells do not cure Alzheimer’s, the objective of this medical approach is to generate new healthy brain cells in large quantities fast enough to help slow progression of the disease and sustainably improve brain function in a way that traditional treatments have not been able to.
Meet Our Doctors & Nurses
Their combined decades of experience in regenerative medicine, sports medicine, alternative treatments, and surgical specialties make our doctors uniquely qualified to develop precision-based medical protocols using mesenchymal stem cells.
Dr. Decio Bars
Chief Medical Director
Dr. Yael Ochoa
Medical Doctor
Carolina Becerra
Registered Nurse
Request an in-person or virtual consultation with a medical specialist to review medical history, lab results, MRIs, and determine eligibility for stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease.
Contact a medical specialist
Put your newfound knowledge about alternative medicine treatments to good use. The next step is to complete our secure medical intake form online to request a consultation with a doctor.
The healing of the future is within your reach! We’re very excited for you and will be at your side every step of the way.