Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
Clinical advances are already using stem cell therapy to treat diabetes types 1 and type 2. Since mesenchymal stem cells have the innate ability to turn into any cell of the body, this therapeutic approach intends to make insulin-producing cells in limitless supply, repair blood vessel lining, and sustainably restore proper insulin levels to reduce dependency on insulin medication. That is why stem cells are becoming a viable and sought-after treatment for diabetes.


Alternative Medicine By Bars has been featured on:




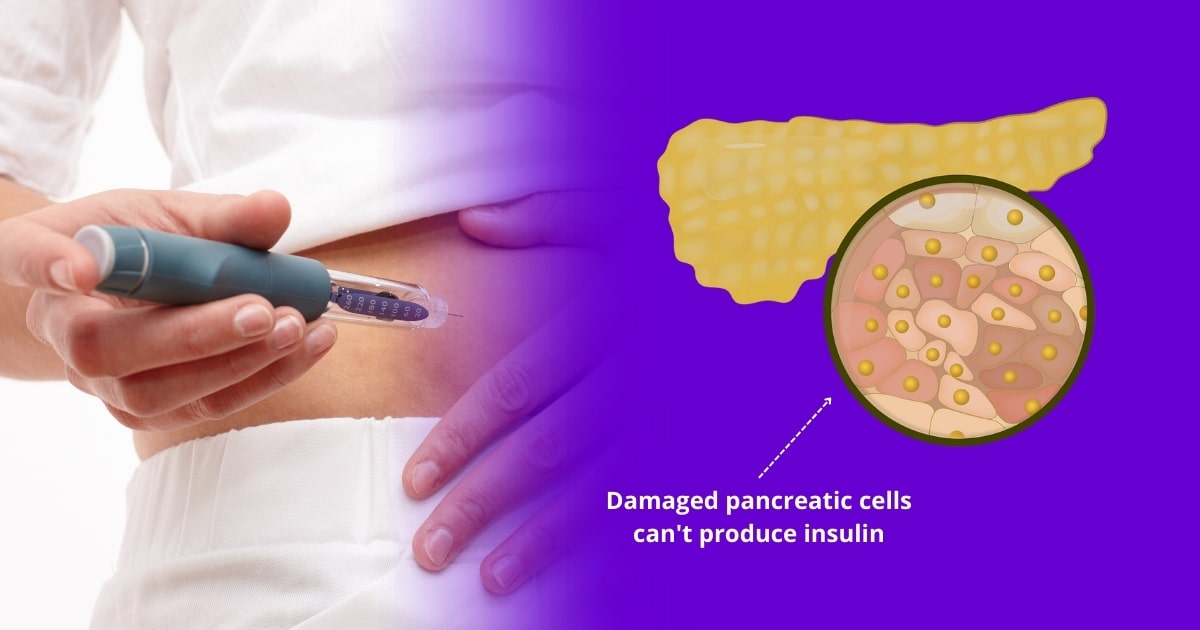
Diabetes is a chronic disease that results in too much glucose in the blood and can lead to serious complications
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that affects how the body uses blood sugar (glucose). A diabetic patient’s body doesn’t make enough insulin cells, or it fails to use it properly. When this happens, sugar in the bloodstream cannot be used for energy so it builds up. Over time, it can lead to heart disease, kidney disease, and blindness. For this reason, patients with diabetes have to monitor their blood sugar levels throughout the day and may need daily insulin injections to survive.
There are different types of diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, but they all can lead to excess blood sugar. Prediabetes and gestational diabetes may be potentially reversible, whereas type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are considered chronic conditions. Of the 537 million people worldwide who have diabetes, approximately 5-10% have type 1 diabetes and about 90-95% have type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetics don’t produce sufficient insulin and need to take insulin every day to survive. Type 1 is more common in children, teens, and young adults. Type 2 diabetics don’t use insulin properly and have difficulty keeping blood sugar levels balanced. Type 2 diabetes develops gradually over years, so it is most common in adults over 40 years old. Prediabetic patients have higher than normal blood sugar levels and may be at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and may disappear after the baby is born.
There is no cure for diabetes yet, but clinical trials have been approved in humans to use stem cells to treat diabetes type 1 by replacing the insulin beta cells that are destroyed by the immune system in type 1 diabetes. Stem cell therapy could also be used to treat type 2 diabetes by promoting the optimal use of insulin and glucose in the body.
What causes Diabetes?
The exact cause of diabetes is unknown.
- Type 1 diabetes often develops fast and no one knows how to prevent it. It is believed that type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction (where the body mistakenly attacks its own cells). The immune system mistakenly destroys insulin and soon the body stops making insulin due to this. Most common in children and young adults. Patients with T1 need to replenish insulin levels every day to survive.
- Type 2 diabetes develops over many years and symptoms appear gradually, so it can remain undetected until adulthood. With type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t use insulin properly and has difficulty maintaining normal blood sugar levels. T2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed by maintaining a healthy weight, keeping a good diet, and being physically active.
- Prediabetes may go away with healthy lifestyle changes.
- Gestational diabetes may go away after the baby is born.
The extent of the impact diabetes has on one’s life is evident in the life-sustaining processes that it affects.
In nondiabetic patients, the body converts most food into sugar (glucose) and transports it to the muscles for energy via the bloodstream. Insulin-β (beta) cells of the pancreas function as the key or passcode that allows glucose to enter cells and be used for energy. Glucose is the brain’s main source of fuel and it is also a vital source of energy for muscle and tissue cells.
But for diabetic patients, insulin is not being produced or the body is unable to use it properly. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells, so the cells suffer and the sugar builds up in the bloodstream. Without this energy source, serious complications can occur. And as sugars build up in the veins, blood thickens, causing the heart to pump harder, and the body to try to get rid of excess sugars. This domino effect can lead to life-threatening complications.
What are the symptoms of Diabetes?
Excessive Glucose
Excessive thirst, hunger, sweating, weakness, tiredness, drowsiness, irritability, mood changes
Physiological Effects
Urinating often, bedwetting, abnormal weight loss in type 1, abnormal weight gain in type 2, high blood pressure and rapid heart rate, blurred vision, nerve damage in feet and hands
Immunological Symptoms
Slow wound healing, propensity for periodontal infections, skin infections, vaginal infections
Request an in-person or virtual consultation with a medical specialist to review medical history, lab results, and determine eligibility for stem cell therapy for diabetes.
Can stem cells be used to treat Diabetes?
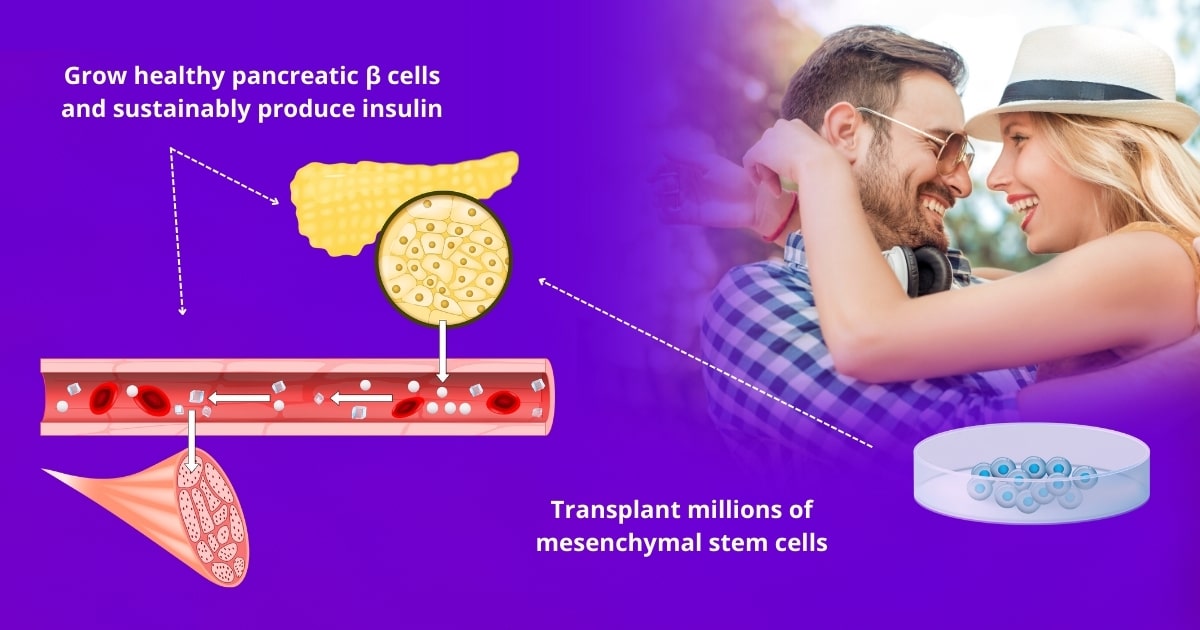
Mesenchymal stem cells can make a limitless supply of fully functional insulin-producing cells without the need for immunosuppressants
Doctors in the USA have already proven that transplants of beta cells from deceased donors and human stem cells could successfully treat type 1 diabetes. There are a few problems with this approach as you can imagine… Ethical concerns raised. There aren’t enough qualified donors to make this treatment become mainstream. Most notoriously, with transplanted adult beta cells, the receiving patients’ immune systems end up attacking the beta cells because it sees them as a foreign invader—and then patients have to live on immunosuppressor medication for the rest of their lives. We need our immune system, so no wonder this method isn’t taking root!
In sharp contrast, our mesenchymal stem cell therapy changes all of that. It has been demonstrated that one can make a limitless supply of fully functional insulin-producing cells from stem cells. Stem cell treatment for diabetes may involve intravenous and localized injection of up to 800 million vibrant pluripotent stromal mesenchymal stem cells (ideally 3 million MSCs / kg of body weight) as well as alternative and regenerative treatments. These stem cells have the potential to grow into new healthy pancreatic cells—including beta cells. Thus, we can generate an unlimited supply of insulin-producing beta cells to reduce or eliminate the need for insulin-replacement medication and without the need of life-long immunosuppressants (because your immune system recognizes them as your own).
Ethics & safety
Are marrow-derived stem cells ethical and safe for diabetes?
Cellular transplant therapy for type 1 diabetes has already yielded positive results in humans. Stem cell therapy for diabetes using mesenchymal stem cells holds immense promise for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. The use of stem cells for diabetes has now evolved to greater FDA approval in human studies.
7 months after a one-time infusion of stem cell derived beta cells, one patient who had lived with diabetes for over 40 years was able to reduce the amount of insulin he injects by 92% and kept an average blood glucose level of 146 mg/dl.
The Edmonton protocol—which transplants islet cells from deceased donors—resulted in the first patients to come off insulin meds for at least 1 year, with one patient remaining insulin-free for more than 20 years. This protocol is already available in a few medical centers today.
However, since the procedures conducted by Vertex Pharmaceuticals use embryonic stem cells (from discarded human embryos), ethical concerns are raised, making them more difficult to develop and be adopted in the future. The Edmonton protocol is rare due to the limited number of donors. The caveat of both procedures is that recipients must commit to a life-long regimen of powerful immunosuppressive drugs that leave them vulnerable to infections and other serious complications.
In contrast, stem cell therapy for diabetes at Alternative Medicine By Bars uses mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow (of the patient or a qualified donor) have demonstrated remarkable cellular differentiation capabilities without the above ethical concerns. Since MSCs are undifferentiated and pluripotent, they are considered immune-privileged. Immune-privileged means that these MSCs are not rejected by the recipient’s immune system and will not force patients to take immunosuppressants for the rest of their lives. This is the type of stem cell for diabetes you can receive at Alternative Medicine By Bars.
Federal regulations
Is it legal to get stem cells for diabetes?
Yes, our clinic is federally licensed, so all of our treatments are legal and are performed by qualified medical professionals. Other clinics get stem cells delivered from a third-party lab which causes degradation of stem cells through hours of transit. Because we would never jeopardize patients’ wellbeing or our long-standing reputation, we have our own private laboratory to harvest and administer stem cells immediately upon preparation to ensure maximum bioavailability for our patients.
Our private laboratory abides by the and application centers abide by the highest international standards such as COFEPRIS and ISO class 5 and 6. Our clinic is accountable to the COFEPRIS and strictly adheres to proven clinical standards.
Long-lasting results
Do stem cells work for diabetes?
Stem cells don’t do miracles, but they are a potential long-term, sustainable alternative to insulin-replacement medication. Patients from all over the globe have successfully received stem cell therapy to improve the pancreatic islet function and regenerate blood vessel lining. Now this therapy is available to you too.
Private Healthcare
Does insurance cover stem cells?
Insurance companies usually do not cover stem cell therapy unless they are for treating certain blood disorders such as a transplant of bone-marrow stem cells to treat leukemia.
It’s important to note that many European and Asian countries have advanced treatments not currently approved for use in the USA. As news spreads about athletes, celebrities, and prestigious professionals undergoing stem cell therapy, treatments options are likely to become less accessible and increasingly privileged.
Unburdened by profit-driven insurance companies, our doctors are able to stay committed to their oath-bound responsibility and never perform unnecessary treatments under the pretense of securing funding. We perform extensive lab work to determine patient eligibility and identify the best application technique and the right quantity of stem cells that will benefit each patient individually.
Thanks to advances in medicine and scientific research, private sector stem cell therapy such as this is today more accessible in terms of travel, price, and quality.
Diabetes: Traditional Treatment Compared to Stem Cell Therapy
- Multiple specialties: endocrinologist, nutritionist, general medicine, pediatrician, ophthalmologist.
- T1 & T2: Synthetic insulin medication to regulate glucose levels.
- For Type 1: Anti-diabetic medication.
- Glucose monitoring devices (regularly extract a tiny amount of patients’ blood to test glucose levels)
- For Type 2: Statin medication to decrease the production of harmful cholesterol in the liver.
- Low-sugar, low-carb dieting and nutritional counseling.
- Regular physical exercise to lower blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
- Lifestyle changes like weight loss, quitting smoking, avoiding abuse of alcohol.
- JDRF estimates adult patients incur a total cost of $20,000 USD annually in medical expenses and loss of productivity.
Because there is no known cure for diabetes, treatment typically consists of insulin replacement therapy for T1, antidiabetic medication for T2, regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, and self care to reduce risk and symptoms.
- Requires specialist care. May be performed in parallel with current medication.
- Up to 800 million mesenchymal stem cells (from 3 million MSC cells per kilo of weight).
- Grow fully functional insulin-producing cells from stem cells continuously for 6-18 months.
- Unlimited supply of cells that can replace dying or damaged pancreatic islets and recruit local cells to regulate metabolic functions.
- Could reduce insulin medication needs by 92%.
- Strengthens cardiovascular health and lowers blood pressure.
- Flow of glucose and oxygen to the brain improves.
- Optional intravenous treatments to nourish and activate the stem cells.
- Optional therapies such as exosomes to help regulate cellular differentiation.
- Cost ranges from $4000 to $25,000 per treatment. A single treatment could last up to 3 years for some early stages.
A localized infusion and intravenous transplanting of millions of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells has the potential to make trillions of insulin-making beta cells. These cells do not raise ethical concerns and are immune-privileged (meaning your immune system recognizes them as your own), eliminating the need for immunosuppressors.
Meet Our Doctors & Nurses
Their combined decades of experience in regenerative medicine, sports medicine, alternative treatments, and surgical specialties make our doctors uniquely qualified to develop precision-based medical protocols using mesenchymal stem cells.
Dr. Decio Bars
Chief Medical Director
Dr. Yael Ochoa
Medical Doctor
Carolina Becerra
Registered Nurse
Aaron Torres
Registered Nurse
Request an in-person or virtual consultation with a medical specialist to review medical history, lab results, and determine eligibility for stem cell therapy for diabetes.
Contact a medical specialist
Put your newfound knowledge about alternative medicine treatments to good use. The next step is to complete our secure medical intake form online to request a consultation with a doctor.
The healing of the future is within your reach! We’re very excited for you and will be at your side every step of the way.